Question 1: A 0.24 g sample of a compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
Answer: Boron and oxygen compound —> Boron + Oxygen
0.24 g —> 0.096 g + 0.144 g
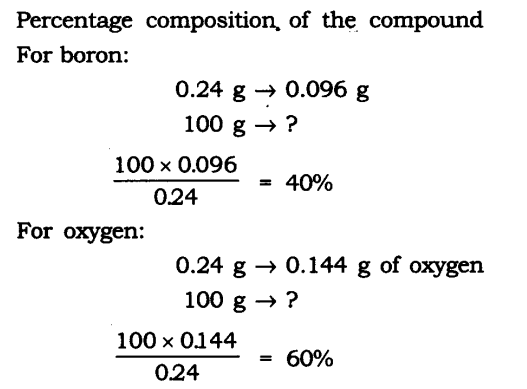
Question 2: When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g of oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
Answer: The reaction of burning of carbon in oxygen may be written as:
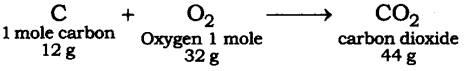
It shows that 12 g of carbon burns in 32 g oxygen to form 44 g of carbon dioxide. Therefore, 3 g of carbon reacts with 8 g of oxygen to form 11 g of carbon dioxide. It is given that 3.0 g of carbon is burnt with 8 g of oxygen to produce 11.0 g of CO2. Consequently, 11.0 g of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.0 g of C is burnt in 50 g of oxygen, consuming 8 g of oxygen, leaving behind 50 – 8 = 42 g of O2. The answer governs the law of constant proportion.
Question 4: Write the chemical formulae of the following:
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium carbonate
Answer:
(a) Magnesium chloride
Symbol —> Mg Cl
Charge —> +2 -1
Formula —> MgCl2
(b) Calcium oxide
Symbol —> Ca O
Charge —> +2 -2
Formula —> CaO
(c) Copper nitrate
Symbol —> Cu NO
Charge —> +2 -1
Formula —> Cu(NO3)2
(d) Aluminium chloride
Symbol —> Al Cl
Charge —> +3 -1
Formula —> AlCl3
(e) Calcium carbonate
Symbol —> Ca CO3
Charge —> +2 -2
Formula —> CaCO3
Question 5: Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds:
(a) Quick lime
(b) Hydrogen bromide
(c) Baking powder
(d) Potassium sulphate
Answer:
(a) Quick lime —> Calcium oxide
Elements —> Calcium and oxygen
(b) Hydrogen bromide
Elements —> Hydrogen and bromine
(c) Baking powder —> Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Elements —> Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen
(d) Potassium sulphate
Elements —> Potassium, sulphur and oxygen
Question 6: Calculate the molar mass of the following substances.
(a) Ethyne, C2H2
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 (Atomic mass of phosphorus = 31)
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3
Answer:
(a) Ethyne, C2H2 = 26 g
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8 = 256 g
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 = 124 g
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl = 36.5 g
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3 = 63 g